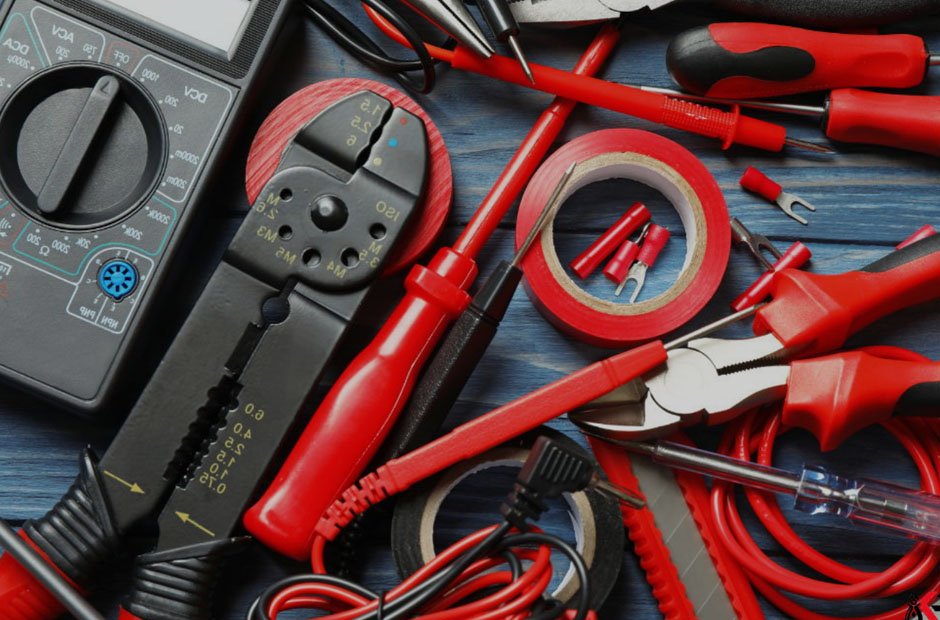
Key Takeaways
- Insulated tools are essential for worker safety, providing certified protection against electrical shocks and arc flash hazards.
- Proper selection, certification, and adherence to regulatory standards such as OSHA and NFPA 70E reduce liability and reinforce a culture of safety.
- Regular training ensures that workers understand the limitations of tools, proper usage, and safety protocols.
- Routine inspection, maintenance, and proper storage preserve tool integrity and maximize protection.
- Integrating insulated tools into safety programs improves operational confidence, efficiency, and overall workplace safety.
Introduction
Worker safety around electrical hazards is a non-negotiable priority in every industrial, commercial, and maintenance environment. Whether in utility services, manufacturing plants, construction sites, or data centers, workers regularly face the dangers posed by energized equipment and unpredictable electrical currents. A key step in safeguarding electrical workers, beyond just adhering to common best practices, is integrating insulated tools into your electrical safety program. These highly specialized tools, designed with robust non-conductive materials, offer protection against electrical shocks and arc flash injuries, greatly reducing on-the-job risks where the environment is unforgiving and mistakes can be fatal. To understand the significance and proper usage of these tools, learn more here: https://divergentalliance.com/insulated-electrical-tools-and-sockets/. Unlike ordinary hand tools, which often have plastic or rubber grips that provide only a false sense of security, insulated tools are rigorously tested to specific electrical standards, such as ASTM and IEC. Each tool is tested for performance under high-voltage conditions, providing a certified line of defense for workers. Implementing them in your safety strategy isn’t just about compliance—it’s a proactive investment in your workers’ wellbeing, substantially minimizing risks while ensuring your company’s operational integrity. Companies that make safety a central value consistently outperform those that do not, as productivity improves and liability decreases.
Understanding Insulated Tools
Insulated tools are engineered with non-conductive materials—typically using high-dielectric plastics and insulation casings—that serve as a physical barrier between the worker and any potentially live electrical currents. Each tool is individually tested to withstand voltage levels—usually up to 1,000 volts AC and 1,500 volts DC—ensuring safety in high-risk scenarios where electrical arcs or accidental contact might occur. This critical safety distinction means that even tools with rubber grips don’t offer real electrical protection unless they have been specifically rated, independently tested, and clearly marked as insulated by the manufacturer. Never substitute a standard tool in environments where voltage hazards exist, as only genuine insulated tools confer layered protection against both expected and unexpected electrical events.
This critical layer of safety guards against faults like accidental contact with energized components, misplaced tools falling onto live parts, or inadequate grounding, which could otherwise result in serious injuries or fatalities. The use of incorrectly rated tools is a leading cause of electrical accidents. Before choosing insulated tools, always confirm they are certified by relevant bodies, such as ASTM or IEC, and carefully check for ratings stamped on each tool. Investing in certified equipment is a decision that can mean the difference between a close call and a life-altering injury.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance
Meeting regulatory standards is not only the legal baseline but also demonstrates a visible commitment to a safe and proactive workplace. Companies that ignore or cut corners on compliance may save money in the short term but expose themselves to long-term risks, including injuries, lawsuits, fines, and reputational damage. OSHA requires insulated tools in any setting where workers are exposed to electrical hazards, both as a preventive measure and as a precondition for more advanced electrical work. Additionally, the NFPA 70E standard outlines comprehensive requirements for electrical safety, emphasizing the necessity of properly selected, labeled, and maintained insulated tools. Adherence to these standards not only reduces liability but also deeply ingrains a culture of safety within an organization. Workers take their cues from leadership, so visible investment in proper safety equipment pays dividends with stronger engagement and safer practices.
Benefits of Using Insulated Tools
- Enhanced Worker Protection:With superior electrical insulation, these tools dramatically reduce the chance of shock or arc flash events, which can result in serious injury, burns, or even fatalities. The right tools act as a last line of defense when all other engineering and administrative controls either fail or are not appropriate for the job.
- Regulatory Compliance:They ensure consistent adherence to OSHA and NFPA 70E, protecting both employees and the company from costly penalties or citations. Keeping up with regulations is not just about avoiding fines—it’s about fostering a responsible work environment that attracts and retains skilled professionals.
- Operational Confidence:Workers properly equipped with insulated tools are more secure, which fosters efficiency and reduces workplace anxiety. The peace of mind that comes from knowing company leadership has invested in top-tier equipment is invaluable, leading to higher morale and lower turnover.
Implementing Insulated Tools in Your Safety Program
- Conduct a Hazard Assessment:Thoroughly identify activities and environments where electrical hazards are present and determine where the use of insulated tools is mandatory. This step is critical for capturing both routine and infrequent tasks, ensuring comprehensive protection.
- Select the Right Tools:Opt for products that carry proper certification, meet the required voltage ratings, and feature ergonomic construction tailored to the task. Regularly review and update your inventory to match new hazards, changing standards, and evolving worker needs. This ensures both versatility and an uncompromised approach to safety.
- Deliver Comprehensive Training:All workers should receive thorough training in the application, limitations, and unique safety properties of each tool to minimize incidents of misuse or accidental exposure. Simulations, practice drills, and regular refresher courses help embed knowledge over the long term.
- Enforce Inspection and Maintenance Protocols:Regularly schedule inspections to identify and remove faulty or worn tools, keeping only safe equipment in circulation. A faulty tool, whether through surface cracks or loss of dielectric strength, becomes a liability rather than an asset.
Training and Education
Correct tool usage and care are only possible with rigorous, ongoing training. Workers need more than just a toolbox—they require a practical understanding of how to use each tool, why specific safety features are in place, and the importance of routine checks. Training covers:
- Why insulated tools are essential and the life-saving difference they provide in hazardous environments, particularly for those working on live circuits or in unpredictable conditions;
- The correct way to handle, use, and store each tool, maximizing their lifespan and safety benefit, including cleaning best practices and tips for avoiding common forms of wear or damage;
- The importance of examining each tool for visible damage prior to use, such as cuts, cracks, or worn insulation that could compromise its effectiveness. Proper documentation of daily pre-use checks reinforces accountability across your team.
Continuous safety education keeps staff informed on emerging hazards and ensures compliance as standards and best practices evolve. Monthly safety meetings, digital learning modules, and toolbox talks all help keep the subject relevant and top-of-mind.
Maintenance and Inspection
Routine care for insulated tools is essential to maintain their protective qualities and maximize your investment. Essential elements of an effective maintenance plan include:
- Regular visual checks for surface damage, including cracks, pitting, or discoloration that may indicate compromised insulation or previous tool abuse. These inspections should be standardized and documented as part of your broader asset management program.
- Electrical retesting per manufacturer recommendations or after suspected tool compromise—such as after a drop from height, exposure to chemicals, or seeing visible wear. Only certified equipment should be brought back into service after passing these tests.
- Storing tools properly—in dry, temperature-controlled environments, out of direct sunlight, and in protective cases when possible. Poor storage practices can degrade insulation materials over time, reducing the reliability of your entire safety program.
Failing to maintain tools can nullify their protective properties, turning a preventative measure into a potential risk and increasing danger for the entire team.
Final Thoughts
Integrating insulated tools into an electrical safety program isn’t merely a regulatory checkbox—it’s a proactive safety strategy that protects lives, ensures compliance, and sustains productivity on any site where electrical hazards are present. By selecting the right tools, adhering to standards, prioritizing ongoing training for workers, and maintaining diligence, organizations can cultivate a safer, more confident workforce equipped to address current and future challenges in electrical maintenance and construction. Leadership commitment, coupled with employee buy-in, transforms insulated tool programs from a compliance measure into a culture of protection and shared responsibility.